Describe the Two Major Types of Active Transport
This pump is actually a structure called a cell membrane pump and it uses energy to transport. Passive transport occurs spontaneously through diffusion which is the movement of chemicals across the cell membrane from regions of higher concentrations to lower ones.
In endocytosis the cells absorb large solid particles and then deposit them into a.

. Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by means of pockets throughout the cell. ATP is converted to ADP during active transport by a membrane-bound Na. Channel and carrier proteins transport material at different rates.
Active transport pumps molecules or substances against a concentration gradient using cellular energy. Primary active transport In this process of transportation the energy is utilized by the breakdown of the ATP Adenosine triphosphate to transport molecules across the membrane against a concentration gradient. Exocytosis is the process through which many cells release a large amount of material.
Moves ions and other solutes against the concentration gradient. Active transport of Na and K through the membranes of nerve cells and erythrocytes requires ATP and ATP cannot be replaced by other nucleoside triphosphates such as GTP UTP and ITP. Describe the two major types of active transport.
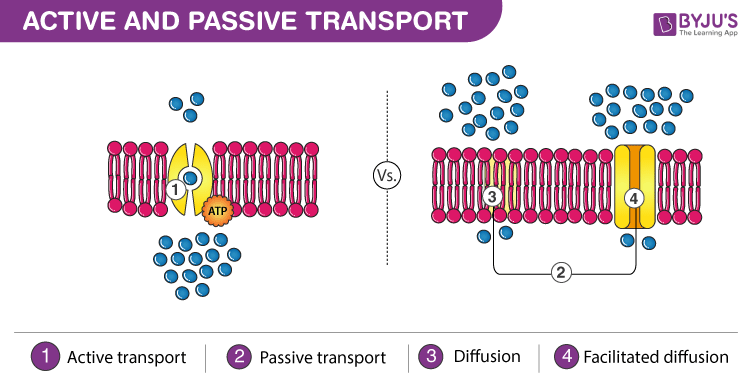
Active and passive transport are the two systems of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. In these descriptions channel diffusion is considered a passive process that involves the ions and charged particles moving through a specific channel protein or. The two major types of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis.
However it is semipermeable due to which certain substances can still move in and out of the cell. Active and passive transport processes are two ways molecules and other materials move in and out of cells and across intracellular membranes. A gradient produced by the combined forces of the electrical gradient and the chemical gradient.
Endocytosis Exocytosis Proton pumps and Sodium-potassium pumps are the kinds of active transport while Osmosis and Diffusion are the kinds of passive transport. Simple channel and facilitated. In secondary active transport the electrochemical gradient is.
Secondary active transport uses the energy stored in these gradients to move other substances against their own gradients. The two major types of active transport are endocytosis and exocytosis. A type of active transport that moves substances including fluids and particles into a cell.
Primary Active transport Secondary Active transport. In primary active transport ATP is used in form of the energy. The method of transporting material that requires energy.
This is the opposite of diffusion and these molecules are said to flow against their concentration gradient. Sodium potassium pump Bulk transport phagocytosis and pinocytosis Cell Membrane Transport The structure of the cell membrane is designed so that it does not allow free movement of substances. Channel proteins transport much more quickly than do carrier proteins.
The main types of cellular transport are passive transport and active transport. Active transport requires energy and involves special proteins called pumps and transporter proteins. Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by means of pockets throughout the cell.
From areas of lower to higher concentrations. During active transport molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Endocytosis and exocytosis are examples of active transport mechanisms Examples of Active Transport Sodium Potassium Pump One of the most important active transport proteins in animals is the sodium-potassium pump.
Active transport is called active because this type of transport requires energy to move. The electrochemical gradients set up by primary active transport store energy which can be released as the ions move back down their gradients. Primary Active Transport Active transport of small molecules that directly uses ATP as an energy source Secondary Active Transport Active transport.
Types of Active transport There are two types of active transport namely Primary active transport and secondary active transport. There are two types of Active transport. The Sodium-Potassium pump Exocytosis and Endocytosis.
Three Main Types of Active Transport Sodium Potassium Pump. Some experts list three types of diffusion instead of two. The main three types of active transport are.
Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against a concentration gradient from an area of lower to higher concentration which does not ordinarily occur so enzymes and energy are required. Features of Active Transport. There are three main types of Active Transport.
Up to 24 cash back Active Transport Active Transport is the term used to describe the processes of moving materials through the cell membrane that requires the use of energy. Exocytosis is the process through which many cells release a large amount of material. Processes of releasing contents of the cell to the external environment.
A different group of carrier proteins called glucose transport proteins or GLUTs are involved in transporting glucose and other hexose sugars through plasma membranes within the body.
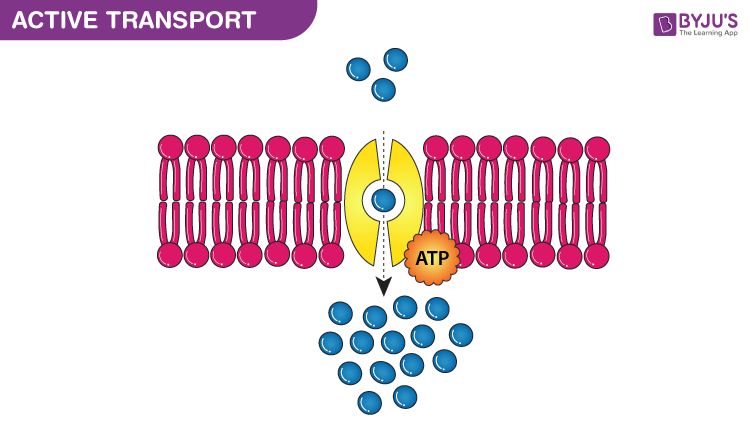
Active Transport Definition And Types Of Active Transport

No comments for "Describe the Two Major Types of Active Transport"
Post a Comment